MolMeDB RDF
WARNING - new RDF schema has been deployed and documentation is being updated at the moment.
Published: December 6, 2022
Version: 1.0
Author: Dominik Martinát
MolMeDB dataset is (not only) accessible in RDF format, enabling the use of Semantic Web capabilities, including SPARQL querying, database integration, use of graph algorithms etc. The semantic web can be seen as a web of data, extending the classical web (web of documents), where the data is represented via terms linked by properties, both defined by ontologies.
What is RDF
RDF (Resource Description Framework) is a set of specifications introducing language for representing information about resources. Resources can be anything from unique physically existing objects to abstract concepts. To know which resource is described, we need to identify it first, and for this purpose are used Internationalized Resource Identifiers (IRI). A common subset of IRIs is URLs identifying web resources.
IRI vs. URI
Sometimes the term URI (Universal Resource Identifier) is used instead of IRI in literature and documents. URIs are subset of IRIs limited to US-ASCII characters in the identifier. All IRIs used in MolMeDB RDF dataset are also valid URIs.
In RDF documents, resources are described via triples, consisting of subject, predicate and object (see Figure 1). Each triple asserts that the subject has some property (predicate) with a value (object). A set of RDF triples creates an RDF graph, and collections of such graphs are called RDF datasets. An RDF graph can be visualized as a node and directed-arc diagram, in which each triple is represented as a node-arc-node link.
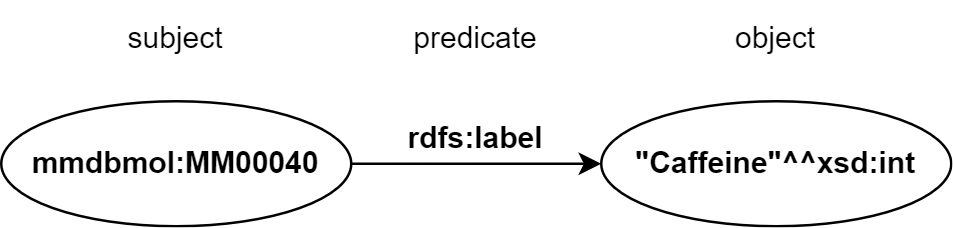
Figure 1. Example of an RDF graph consisting of a single triple. The graph represents the relationship of a resource (subject) identified by IRI having a label (predicate) with a “Caffeine” value (object).
As subject can be IRI or a blank node, but the predicate must be an IRI value. The object can represent IRI, blank node or some literal value (e.g. natural language string, number or time value). Blank node in a triple represents an entity with a given relationship, which exists without a specific name.
RDF is an abstract format and RDF datasets can be expressed in many different serializations, some of which are RDF/XML, Turtle or N-Triples.
What can RDF do for you
RDF serializations are machine-readable; for example, RDF/XML can be parsed as any XML document. However, RDF datasets offer much more. The main advantage of RDF is the possibility of graph merging via nodes identifying the same resource by the same IRI. MolMeDB RDF uses this to link compounds to their counterparts in PubChem, ChEMBL, ChEBI and wwPDB, transporter proteins to UniProt and some membrane components to ChEBI. MolMeDB RDF dataset can be downloaded and then imported into a triplestore where it can be queried using a SPARQL query language. The dataset can also be merged with other datasets (e.g. PubChem RDF) using the common IRIs. Another way of querying MolMeDB RDF is by online SPARQL endpoint, allowing federated queries combining multiple datasets served by their SPARQL endpoints. Thanks to cooperation with the IDSM database, the substructure and structural similarity queries using SMILES strings or MOL files are supported. Additionally, the RDF representation of MolMeDB data allows the use of logical inference.
WARNING - dataset downloads linked in this section are still old datasets. New ones will be added soon. SPARQL endpoint services the most recent dataset version.
MolMeDB RDF dataset can be obtained in the following formats:
- RDF/XML
- Turtle
- N-Triples
MolMeDB RDF SPARQL endpoint is available here.
MolMeDB RDF schema
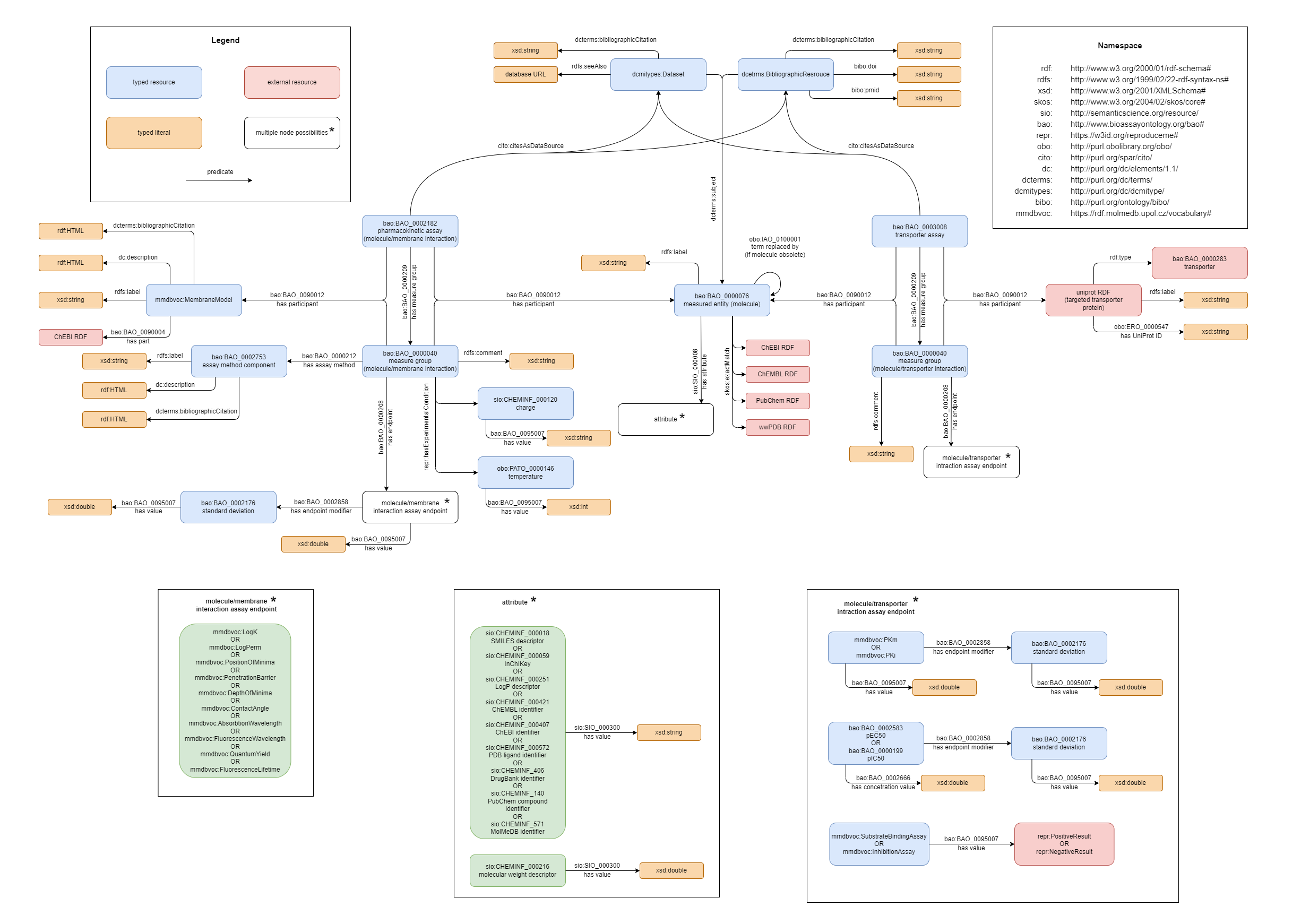
Figure 2. Simplified diagram of MolMeDB RDF schema.